How to Download and Install Appium Desktop on Win and Mac
Appium Desktop is an application for Windows, Macintosh and linux OS. Appium Desktop is a UI based app with a lot of connectivity and configuration options. It will allows the user to view some advanced options in UI like Inspector for identifying elements, Relaxed security, exporting appium logs and so on..
· Using a graphical interface for the Appium Server. You can set options, start/stop the server, see logs, etc… Appium Desktop comes with Node runtime files, so no need to separately download and install Node.
· One of the powerful and main feature on Appium desktop is INSPECTOR. Inspector is the object spy in Appium (like QTP you can spy an element by clicking). Inspector tool will identify the elements along with ID, XPATH and all applicable attributes.
http://appium.io/ is the official website for Appium desktop. One can easily download the latest desktop build of Appium form Downloads sections. Based on preferred the OS we can easily download the build. Hence it is an open source we can download and use it free of cost.
For Windows:
If you are using Windows based OS, then you have to download the .exe file. (ex: Appium-windows-1.15.1.exe). Once downloaded you can install the software by double clicking on the exe file.
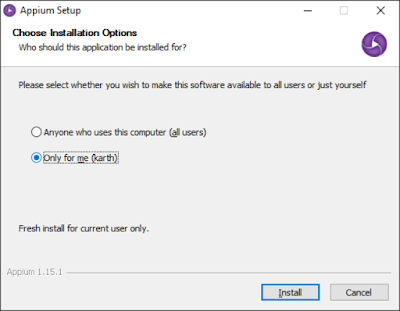
On double click on exe file, the below installation screen will popup
Select the 1st radio button if you want appium to be avaialbe for all user who logs in this computer. Else click on 2nd option. On clicking on “Install” button, installation will begin
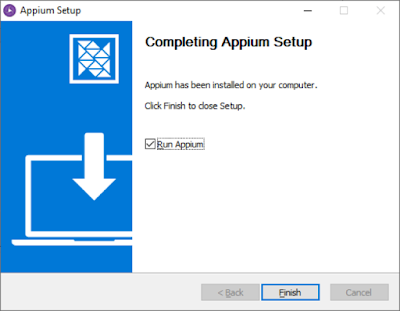
Click on “Finish” button to launch the Appium desktop and also to complete the installation process and to quit the installation wizard.
For Mac:
If you are using Mac OS, then you have to download .dmg file so that you can simply move the file under Application to get started. (ex: Appium-mac-1.15.1.dmg). Once downloaded you just need to extract the file and move the build to Applications.
Just click and drag the appium logo to Applications.
Appium also available as an AppImage for Linux. App image is like an executable file for windows. Here in linux no need to install the build, just we need to open the appImage so that your Appium server UI will be prompted.
The good thing in Appium desktop is no UI change for any operation system. UI is built to be stable across platform.
Now we are ready with our Appium desktop to launch and starting the server.
Launching Appium Desktop after Installation for the first time:
Appium desktop UI is very simple and easy to access. Below image represents the home page of Appium Desktop.
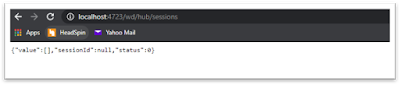
In Simple Mode, one can start the Appium server by providing the “Host” and “Port” values. By default Appium REST http interface listener will use the Host 0.0.0.0 and Port “4723”. If any other programs like Jenkins/tomcat are running on a default local server/port then we can change the Port in Appium.
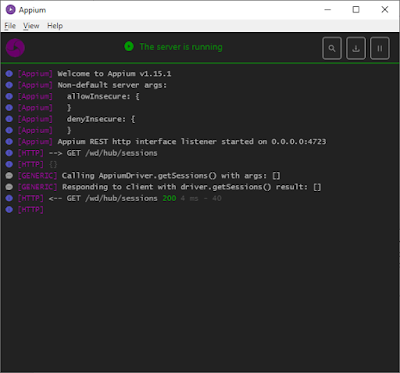
Clicking on “Start Server” button will initiate a local host server with the given port #. You can start seeing logs in Appium desktop like below.
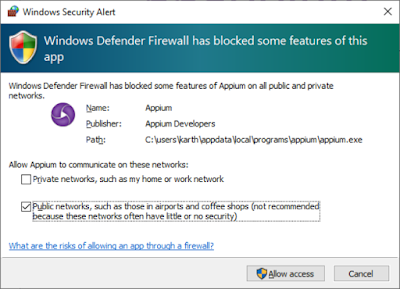
By any chance if your firewall is blocking Appium or if you get the below screen, select any or both the checkboxes and click on “Allow access” button. So that Appium can initiate a local host.
How to connect to an Emulator or a real Device with Appium:
Connecting a real device with Appium is very simple. Appium Desired Capabilities will take care of all the connectivity protocols. But before trying to connect we need to make sure all prerequisites are available in the computer. It’s all about configuration and SDK’s
If you want to connect an Android device on a Windows/Mac based OS, then you have to download and install the Android Studio/ Android SDK. Without Android SDK Appium cannot initiate a connectivity to any android based devices. The reason behind this is, Appium will connect to android device in developer debugging mode. Hence to enable the debugging mode “SHELL” commands are inevitable, Commands like ADB, Shell are available only on Android SDK. So to make a connectivity to a real android device “Android SDK” is must.
You can download Android SDK on its official website https://developer.android.com/studio. Based on the OS you can download and set the preferences. Once Android studio is installed it is also necessary to install the android SDK based on the device Android version. Ex. My real device is running Android version 9, then I need to install the SDK for Android 9. This can be achieved by AVD in android studio.
“Please use the below steps for creating an Android Emulator”
Step 1: Open android studio
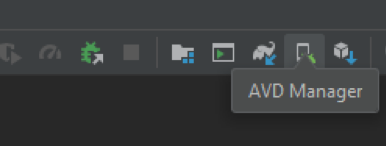
In the home page, you can find “AVD Manager” icon on the top left corner
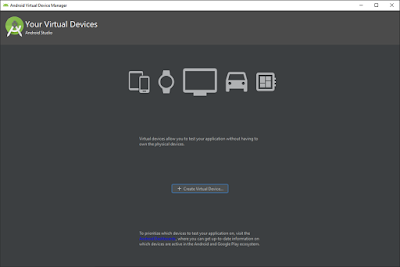
Step 2: Click on “AVD Manager” icon to get the below screen
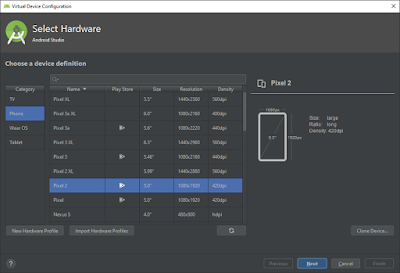
Step 3: Create a Virtual Device (Emulator) by clicking the button “ + Create Virtual Device..” then you will be navigated to the below screen
Select the option “Phone” and you can select any device model based on your real device screen size (if needed) and click on “Next”
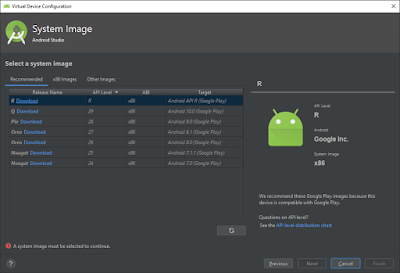
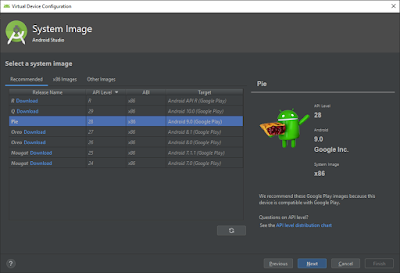
The below screen will list out all the applicable Android version for the selected device. Then you can click on download as per the android version you need.
Here I have selected “Android Pie” and click on Download.
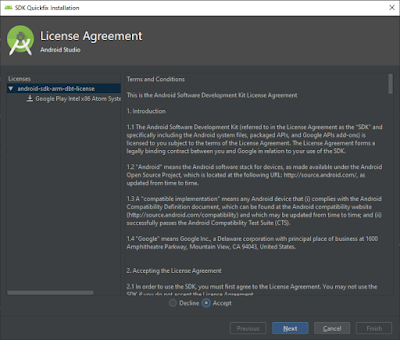
Accept the license Agreement and click on Next button
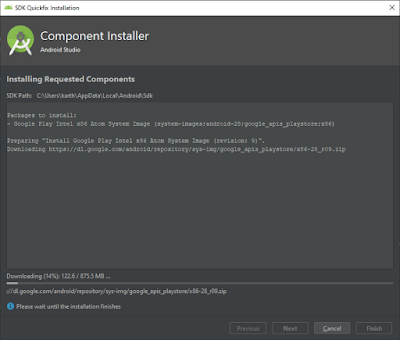
Now the selected Android OS will start to download
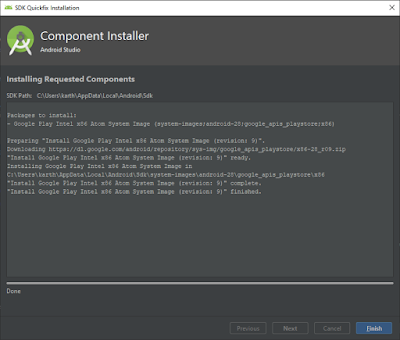
Click on finish once download is completed.
So we are done with downloading SDK and successfully created Android Emulator.
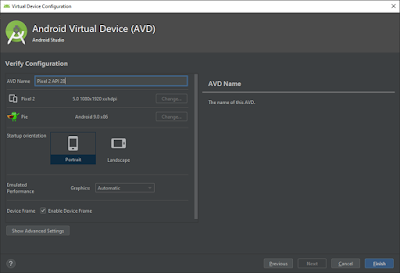
Click on “Next” button to create an Emulator
Provide any name to the Emulator and click on “Finish”.
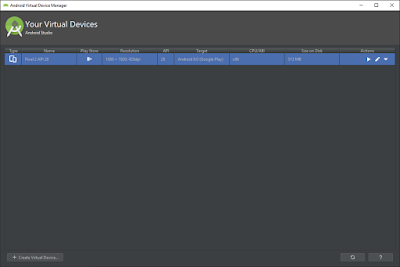
On the next time when you click on “AVD Manager” you will get the below screen where you can see the list of AVD’s created
Click on “Launch this AVD” button (Play button) under Actions section to start the Emulator.
Emulator is launched successfully 😊
2. Android Environmental variables
Once Android SDK is downloaded successfully we can start using ADB and Shell executables from Android SDK. But the problem is windows OS don’t know from where it need to take the executable files. Imaging its like searching a small tool on a big warehouse. So to make the search easier we need to instruct the OS from where we need to utilize the commands, here comes the Environment variables. We need to inform Windows OS to take the executable files from this location and execute my command. So how to configure this ? let’s see
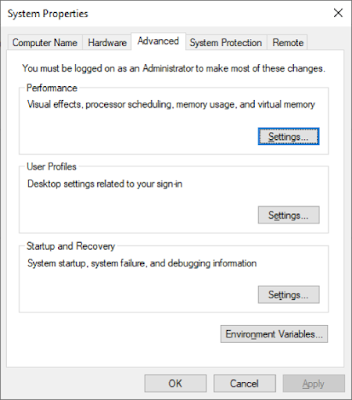
There are many ways to navigate to “Environment Variables” screen, A common way is to click on start menu and type “My Computer” or “My PC”, then right click on that and select the “properties” option form the menu. Select “Advanced System Settings” to get system properties screen
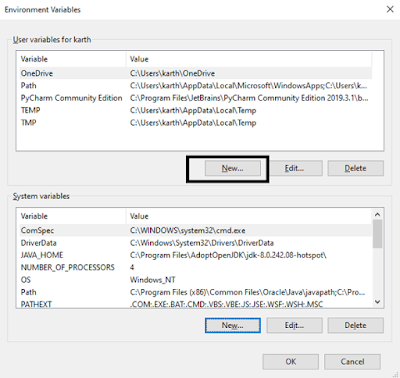
Click on “Environment Variables” and Select “New” button under “User Variables” section
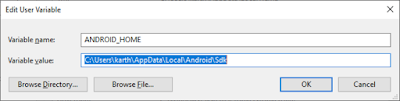
Now, it’s time to create “Android_Home” path. Android_Home is nothing but the parent folder where we have our SDK and Platform tools available. By default the Android_Home path should be
“C:Userscurrent userAppDataLocalAndroidSdk”
Enter the “Variable Name” as “Android_Home” and “Variable value” with the directory value and click on “OK” button to add the record.
Now “%android_home%” command refers to the directory where our SDK files are located.
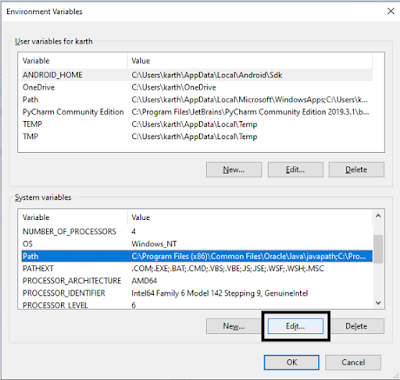
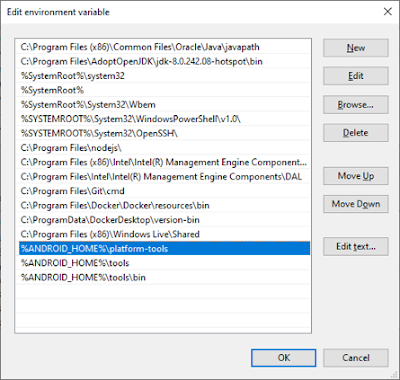
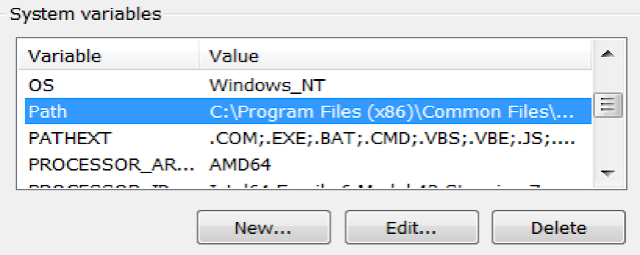
It’s time to add “Platform-tools” and “tools” link to our Sytem variables, under “Path” record. For that click on “Path” record and select “Edit” button under System Variables
As I already mentioned, “%android_home%” refers to our SDK directory, now it’s time to add below 3 directories
%ANDROID_HOME%platform-tools
%ANDROID_HOME%tools
%ANDROID_HOME%toolsbin
Just copy and paste it one by one under “Path” record. Like below,
Now we are done with setting up Environment variables for Android. Click on OK button and close all the open windows.
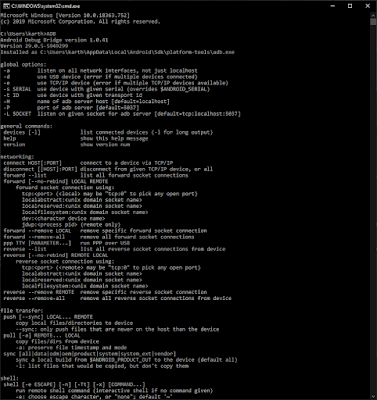
Now open “Command Prompt” and simply type “ADB” and Enter
 If you get the text as mentioned in the image, then you successfully configured the Android SDK variable path in our OS. Now we are good to go with Appium to connect to any real device/ Emulators.
If you get the text as mentioned in the image, then you successfully configured the Android SDK variable path in our OS. Now we are good to go with Appium to connect to any real device/ Emulators.
That’s it!! You are ready to automate 🙂
Cheers!
Naveen AutomationLabs
Blog Contributors:
Author: Ragavendran
Ragav, having 10.5 years of Testing experience on which 7 years of rich experience in automation using UFT, Selenium (Java/Python). Expertise in Web and Mobile automation testing using Appium.
Reviewer: Naveen
 If you get the text as mentioned in the image, then you successfully configured the Android SDK variable path in our OS. Now we are good to go with Appium to connect to any real device/ Emulators.
If you get the text as mentioned in the image, then you successfully configured the Android SDK variable path in our OS. Now we are good to go with Appium to connect to any real device/ Emulators.